Breast Cancer - General Information
Breast cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the breast.
It happens as a result of mutations (changes) in the gene as a result of inherited (from parents) or environmental factors. Risk of breast cancer increases with age and in those who have their first child late or do not breast feed their child adequately.
Symptom of breast cancer may be a lump or change in the breast or axilla
All breast/axillary lumps need a proper clinical examination which would determine whether further testing like imaging (usually mammogram) and FNAC/Core biopsy are required.
All breast cancers are not the same. The biology of the tumor determines the chance to spread to other parts of the body; but this cannot be changed, and so, early detection of the disease is of paramount importance to minimize the risk of disease spreading to distant sites of the body like bones, lung, liver or brain. The best option to detect the cancer at an early stage is to have regular clinical breast examination/tests as recommended by the snehita risk calculator - http://snehita.in/risk
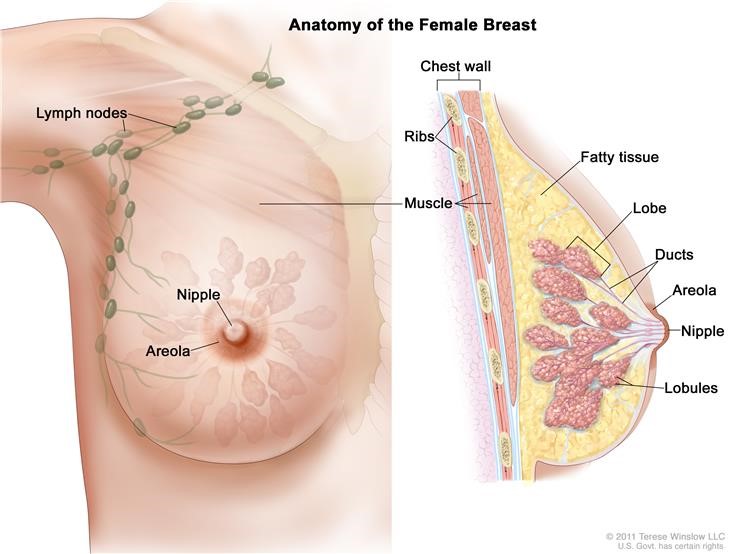
The breast is made up of lobes and ducts. Each breast has 15 to 20 sections called lobes. Each lobe has many smaller sections called lobules. Lobules end in dozens of tiny bulbs that can make milk. The lobes, lobules, and bulbs are linked by thin tubes called ducts.
Breast has blood vessels and lymph vessels. Lymph vessels carry almost colorless, watery fluid called lymph. They carry lymph between lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures found throughout the body. They filter lymph and store white blood cells that help fight infection and disease. Breast cancer usually spreads to groups of lymph nodes found near the breast in the axilla (under the arm), above the collarbone, and in the chest. Rarely breast cancer can present as swelling of the lymph node above collar bone also.
Treatment of breast cancer has to be a planned process. Surgery is the main treatment and cure is not possible without surgery. Surgery on the breast has to be done as the treatment and not for diagnosing breast cancer. Diagnosis has to be made by core biopsy/FNAC prior to Surgery. However, in < 5% cases surgical biopsy may have to be done to reach a diagnosis. In such situations, frozen section (pathological examination to diagnose cancer during surgery) could help to plan surgery as a treatment and not just a biopsy. In very few cases, a second surgery (as treatment) may be required if frozen section cannot diagnose cancer.
After surgery, other treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, endocrine therapy (Tamoxifen/Letrozole) or Biological therapy ( Traztuzumab) may be required to improve the outcome.
In certain situations, Chemotherapy may be advised as the first treatment, especially if the cancer is in an advanced stage. In such situations also cure is possible only if Surgery is done to remove the disease after chemotherapy.
Follow up is required, as these patients have more risk for having a new breast cancer in the other breast, which needs to be detected early and treated by a proper initial surgery. During follow up, some tablets may have to be continued for 5 to 10 years or changed to newer tablets depending on the biology of the cancer.
It is important for breast cancer patients to advise all female relatives to have regular clinical breast examination/tests as recommended by the snehita risk calculator - http://snehita.in/risk
Sometimes the disease would have spread to distant sites of the body and cure may not be possible. In such situations, surgery may not be offered and patient would be having only medical treatment. Surgery is usually done in such situations only to palliate a bleeding or fungating breast cancer. Rarely Curative surgery may be attempted if spread is limited to few areas of the bone only or if it is possible to resect all disease in the body.